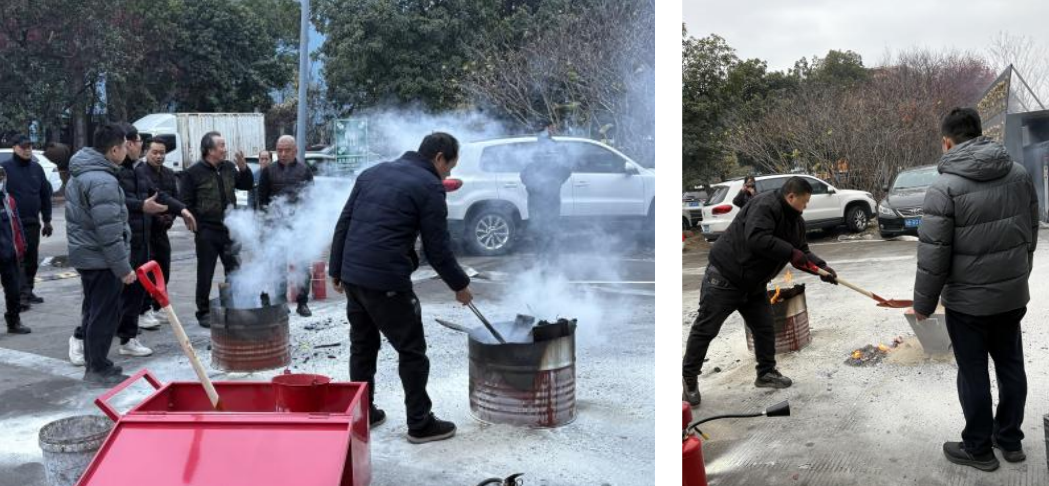
To enhance the emergency response capabilities of all employees and address the fire risks associated with magnesium alloy production, Weituo Company conducted a special fire drill on January 20, 2026, focusing on the differences between practical operation and actual response, and strengthening the safety production defense line. Magnesium alloy fires are Class D metal fires and cannot be extinguished with conventional equipment such as water-based or ABC dry powder extinguishers. Specialized media such as 7501 extinguishing agent and dry sand are required. After extinguishing the fire, the residue must be continuously covered to prevent reignition.
The drill procedure was as follows:
1. Fire Trigger: A simulated spontaneous combustion occurred in the magnesium alloy scrap area of the workshop. Patrolling employees immediately reported the incident and details.
2. Emergency Response Plan Activation: The emergency command center activated the specific emergency plan within 30 seconds, simultaneously issuing various instructions.
3. Personnel Evacuation: The evacuation team guided employees to evacuate in an orderly manner, with all personnel assembled within 10 minutes.
4. Precise Firefighting: The firefighting team, wearing protective gear, used Class D dry powder fire extinguishers to extinguish the fire according to regulations. After the open flames were extinguished, the residue was covered with dry sand to prevent reignition.
5. On-site Warning and Inspection: The warning team established a safety zone, and the safety team conducted a comprehensive inspection of potential hazards before reporting the completed situation.
The company leader reviewed and summarized the drill, affirming the collaborative capabilities of each team and identifying areas for improvement. This drill enabled all employees to master the emergency response procedures and differentiated handling points for magnesium alloy fires, addressing the shortcomings of routine drills in terms of specificity.




 中文简体
中文简体 English
English 한국어
한국어 日本語
日本語 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى

